
In order to disentangle this complex issue, the aims of the present study were to evaluate the burden of symptoms in patients with different Kellgren-Lawrence (K-L) degree of KOA, comparing those with and without BC, and to assess the outcomes after conservative treatments in both groups. Besides authors who claim that the presence of the enlarged bursa may increase the symptoms of KOA, others have not observed any relationship with pain and other discomfort. So, it is debated whether and to what extent each condition contributes to the patient's discomfort.

The location of pain and swelling may be diagnostic, but sometimes it may be difficult to evaluate the exact cause of symptoms. Several symptoms (e.g., pain, swelling, stiffness, loss of flexibility) are common both to KOA and BC. Bursal enlargement and inflammation could be the result of the same factors involved in the pathogenesis of KOA (e.g., multiple micro-traumas due to an excessive loading on the joint, sporting activity, impaired joint stability, meniscal tears, chondromalacia, valgus deformity and others). However, roughly 50% of BCs do not communicate with the knee joint therefore, other mechanisms may be involved. In normal conditions the amount of fluid is small and can be easily reabsorbed on the contrary, in OA (mainly in activated knee osteoarthritis) the amount of fluid is increased and this causes the filling and the formation of popliteal cysts.

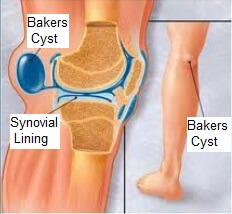
During flexion the “valve” opens and the synovial fluid under pressure moves into the bursa during extension the “valve” closes due to the tension of these muscles and the fluid remains trapped inside the bursa. There is a “valve” effect between the bursa and the joint, due to the action of the semitendinosus and gastrocnemius muscles. The communication channel is a 15–20 mm transverse slit-like capsular opening adjacent to the proximal postero-lateral margin of the medial femoral condyle. This figure is not surprising given that in almost 30–50% of cases a connection is present between the knee articular space and the gastrocnemio-semimembranosus bursa. In these patients the prevalence ranges from 20% to 40%, and increases with age, severity of OA, and duration of disease. It may be detected incidentally in the general population but is more frequently found in patients suffering from knee osteoarthritis (KOA). Sudden onset of diffuse knee pain that is not caused by injury, as well as swelling that is red and warm, can suggest inflammation or infection in the knee.Baker's cyst (BC) results from fluid enlargement of the gastrocnemio-semimembranosus bursa located in the medial aspect of the popliteal fossa. This can occur with a forceful impact or repetitive use. Pain and swelling localised to the kneecap or the inner side of the knee can suggest inflammation of the cushioning fluid-filled sacs called bursa, known as bursitis. Being overweight or obese, previous knee injuries, and doing repetitive or heavy physical activities can increase your risk of developing knee osteoarthritis. Knee pain often worsens with activity and eases with rest.
Side of knee pain from running, cycling, or other activities that involve repeated knee bending often stems from tightness in the ligaments running from your knee up your thigh.Ī common cause of knee pain, particularly in older people, is osteoarthritis -a condition where the cartilage between bones breaks down and causes pain, stiffness and swelling in the knee joint. Knee pain from running or sports that involve a lot of jumping can result from overuse and gradual damage of the tendons attached to the kneecap. Knee pain can also be caused by overuse of the knee joint and can occur during activities such as walking and running. Common symptoms of ligament and meniscus damage include knee pain(usually at its worst during the first 2 to 3 days after knee injury) and swelling (occurs within minutes to days of a knee injury, depending on the underlying damage). Meniscus tears can result from forceful impact or twisting of the knee, especially during weight-bearing exercise, and from wear and tear in older people. Ligament sprains are often caused by sudden twisting of the knee joint, too much force on the knee joint from repeated jumping or sudden stopping while running, or direct impact to either side of the knee. Common knee injuries include sprains and strains(overstretching of the ligaments, muscles, or tendons) and cartilage (meniscus) tears. Knee pain is often caused by a knee injury.

What are common knee pain causes and symptoms?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
